Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering refers to the direct manipulation of DNA to alter an organism’s characteristics (phenotype) in a particular way.
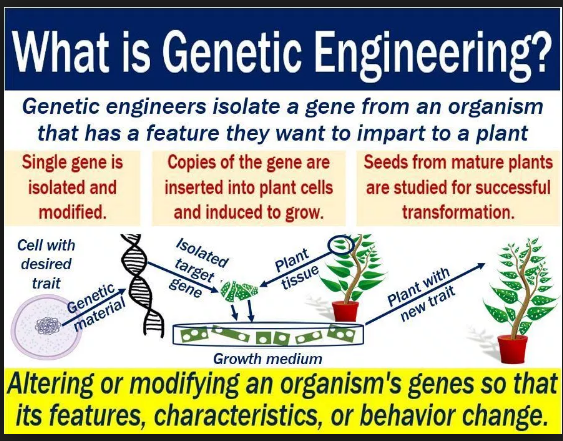
What is genetic engineering?
- Genetic engineering, sometimes called genetic modification, is the process of altering the DNA in an organism’s GENOME.
- This may mean changing one base pair (A-T or C-G), deleting a whole region of DNA, or introducing an additional copy of a gene.
- It may also mean extracting DNA from another organism’s genome and combining it with the DNA of that individual.
- Genetic engineering is used by scientists to enhance or modify the characteristics of an individual organism.
- Genetic engineering can be applied to any organism.
- For example, genetic engineering can be used to produce plants that have a higher nutritional value or can tolerate exposure to herbicides.
Applications of Genetic Engineering
The applications are:
- Application in Agriculture
- Application to Medicine
- Energy Production
- Application to Industries.
Application in Agriculture:
An important application of recombinant DNA technology is to alter the genotype of crop plants to make them more productive, nutritious, rich in proteins, disease resistant, and less fertilizer consuming.
Recombinant DNA technology and tissue culture techniques can produce high yielding cereals, pulses and vegetable crops.
Some plants may even develop their own fertilizers some have been genetically transformed to make their own insecticides.
Scientists have developed transgenic potato, tobacco, cotton, corn, strawberry, rape seeds that are resistant to insect pests and certain weedicides.
Some of the cloned genes include:
- Genes for phaseolin of french bean,
- (ii) Few phaseolin leg haemoglobin for soybean,
- Efforts are being made to improve several agricultural crops using various techniques of genetic engineering which include:
- (i) Transfer of nitrogen fixing genes (nif genes) from leguminous plants into cereals.
- (ii) Transfer of resistance against pathogens and pests from wild plants to crop plants.
- (iii) Improvement in quality and quantity of seed proteins.
- (iv) Transfer of genes for animal proteins to crop plants.
- (v) Elimination of unwanted genes for susceptibility to different diseases from cytoplasmic male sterile lines in crop like maize, where cytoplasmic male sterility and susceptibility are located in mitochondrial plasmid.
- (vi) Improvement of photosynthetic efficiency by reassembling nuclear and chloroplast genes and by the possible conversion of C3plants into C4
- (vii) Development of cell lines which may produce nutritious food in bioreactors.
Application to Medicine:
Genetic engineering plays significant role in the production of medicines.
Microorganisms and plant based substances are now being manipulated to produce large amount of useful drugs, vaccines, enzymes and hormones at low costs.
Gene therapy by which healthy genes can be inserted directly into a person with malfunctioning genes is perhaps the most revolutionary and most promising aspect of genetic engineering. The use of gene therapy has been approved for diseases such as cystic fibres emphysema, muscular dystrophy, adenosine deaminase deficiency.
In one type of gene therapy new functional genes are inserted by genetically engineered viruses into the cells of people who are unable to produce certain hormones or proteins for normal body functions.
Vaccines:
Recombinant DNA Technology is also used in production of vaccines against diseases. A vaccine contains a form of an infectious organism that does not cause severe disease but does cause immune system of body to form protective antibodies against infective organism. Vaccines are prepared by isolating antigen or protein present on the surface of viral particles.
Hormones:
Until recently the hormone insulin was extracted only in limited quantities from pancreas of cows and pigs. The process was not only costly but the hormone sometimes caused allergic reactions in some patients of diabetes.
The human insulin gene has been cloned in large quantities in bacterium E. coli which could be used for synthesis of insulin. Genetically engineered insulin is commercially available as humilin.
Cancer:
Cancer is a dreaded disease. Antibodies cloned from a single source and targetted for a specific antigen (monoclonal antibodies) have proved very useful in cancer treatment. Monoclonal antibodies have been target with radioactive elements or cytotoxins like Ricin from castor seed to make them more deadly. Such antibodies seek cancer cells and specifically kill them with their radioactivity or toxin.
Energy Production:
Recombinant DNA technology has tremendous scope in energy production. Through this technology is now possible to bioengineer energy crops or biofuels that grow rapidly to yield huge biomass that used as fuel or can be processed into oils, alcohols, diesel, or other energy products.
The waste from these can be converted into methane. Genetic engineers are trying to transfer gene for cellulase to proper organisms which can be used to convert wastes like sawdust and cornstalks first to sugar and then to alcohol.
Application to Industries:
Genetically designed bacteria are put into use for generating industrial chemicals. A variety of organic chemicals can be synthesised at large scale with the help of genetically engineered microorganisms. Glucose can be synthesised from sucrose with the help of enzymes obtained from genetically modified organisms.
With the help of genetic engineering strains of bacteria and cyanobacteria have been developed which can synthesize ammonia at large scale that can be used in manufacture of fertilisers at much cheaper costs.
Recombinant DNA technology can also be used to monitor the degradation of garbage, petroleum products, naphthalene and other industrial wastes.
Contact us for:-
-
-
- IAS coaching in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- UKPCS-UKPSC/UPPCS coaching in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- Current Affairs classes in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- For getting detailed feedback on your answers and improve answer writing
- Phone Number:–9997453844
- Telegram channel : click here
-
- Master Uttarakhand Current Affairs for UKPCS: CM Samvad & Monthly PDF Download - February 20, 2026
- UKPSC प्रारंभिक परीक्षा स्टडी मटेरियल 2026 (Upper & Lower) | Oracle IAS - January 3, 2026
- UKPCS 2026 प्री परीक्षा कोर्स : छात्रवृत्ति टेस्ट: Oracle IAS - December 30, 2025
