Viral Infection
A virus is a small infectious organism that replicates only inside the living cell of another organism. A very interesting character of viruses is that they can infect all type of life forms, animals and plants to microorganism including bacteria .When not inside a cell , virus exist as independent particles and these particles are mainly made up of genetic material such as RNA and DNA .This is why viruses have described to be at the edge of life.
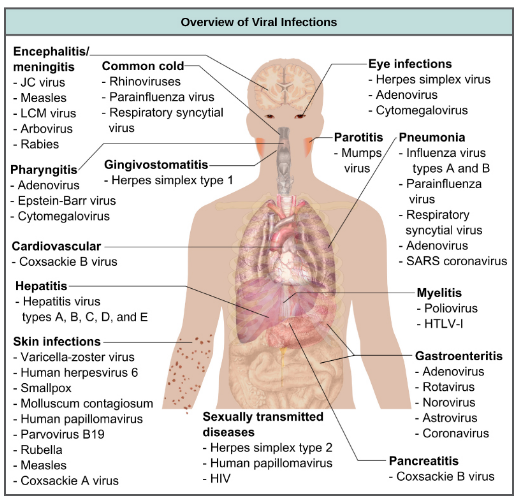
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism body is involved by pathogenic virus, infectious virus particles (virions) attach to an enter susceptible cells.
Viral Infection usually detected by clinical presentation for instance- severe muscle and joint pains, presiding severe or skin rashes and swollen lymph glands.
Some of the common Viral Infection/diseases are – chicken pox, flu (influenza) ,HIV, encephalitis , Hepatitis, Pneumonia ,etc.
-
HIV(Human Immuno Deficiency Virus)
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system , the bodies natural defence system without a strong immune system,the body has trouble fighting of disease.
Both the virus and the infection of causes are called HIV.
White Blood cells are an important part of the immune system.HIV infects and destroys certain white blood cells called CD4+ cells are destroyed. The body can no longer defend itself against infection.
The last stage of HIV infection is AIDS(Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Virus).
People with AIDS have a low number of CD4+ cells and get infections or cancer that rarely occur in healthy people. These can be deadly.
These are of two types:
HIV1: which causes almost all the cases of AIDS worldwide.
HIV2: which causes an AIDS like illness.
HIV infection is caused if you are in contact with infected- Blood semen or Vaginal fluid.
Symptoms
- Common early symptoms are-
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Joint pain
- Swollen glands(lymph nodes)
- Skin rash
- After a certain point these symptoms reappear these include –
- Swollen lymph node
- Extreme tiredness
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Night sweat
Prevention
- Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis
- Postexposure prophylaxis
- Antiretroviral drugs
- Condoms
- Low dead space syringes
-
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is a complex and severe disease that can occur in people of all ages anywhere in the world. It is defined as an inflammation of the brain substance together with evidence of brain dysfunction.
Inflammation has occurred in the brain because something foreign or something abnormal has sparked the immune system into action. This action has resulted in the inflammation.
There are two main types of encephalitis; Infectious Encephalitis and Autoimmune Encephalitis.
The viruses that can cause encephalitis include:
- Herpes simplex virus
- Enteroviruses
- Rabies virus
- Mosquito born virus
- Tick born virus
Symptoms
The symptoms of encephalitis can range from mild to severe.
Mild symptoms include:
- fever
- headache
- vomiting
- stiff neck
- lethargy (exhaustion)
Severe symptoms include:
- fever of 103°F (39.4°C) or higher
- confusion
- drowsiness
- hallucinations
- slower movements
- coma
- seizures
- irritability
- sensitivity to light
- unconsciousness
Infants and young children show different symptoms. Call a doctor immediately if your child is experiencing any of the following:
- vomiting
- bulging fontanel (soft spot in the scalp)
- constant crying
- body stiffness
- poor appetite
Prevention
Treatment for herpes-related encephalitis includes supportive are as well as antiviral therapy with a drug such as acyclovir.
Other treatment may be used to –
Lower fever
Provide hydration
If they develop and reduce any pressure in the skull. Infants and elderly people are at greater risk of sustaining permanent brain damage.
-
Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver. Inflammation is a tissue’s reaction to irritation or injury. It generally results in pain, redness, and swelling.
There are many causes of hepatitis. Viral hepatitis is caused by a virus. Viral hepatitis can either be acute (lasting less than 6 months) or chronic (lasting more than 6 months). Viral hepatitis can be spread from person to person. Some types of viral hepatitis can be spread through sexual contact.
Several viruses are known to cause hepatitis. Common forms of viral hepatitis include:
Hepatitis A: This form of hepatitis does not lead to a chronic infection and usually has no complications. The liver usually heals from hepatitis A within 2 months. However, occasional deaths from hepatitis A have occurred due to liver failure. Hepatitis A can be prevented by vaccination.
Hepatitis B: . More than 70% of all cases of hepatitis B affect young people between the ages of 15 and 39. Most people recover from the virus within 6 months. A few cases cause a life-long, chronic infection. Chronic hepatitis causes ongoing damage to the liver. The earlier in life hepatitis B is contracted, the more likely it is to become chronic.
Hepatitis C: Patients with hepatitis C develop a chronic liver infection. It often does not show any symptoms. No vaccine is yet available to.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of hepatitis include:
- Dark urine (hepatitis A, B, C)
- Stomach pain (hepatitis B, C)
- Yellow skin or eye whites, called jaundice (hepatitis A, B, C)
- Pale or clay-colored stool (hepatitis A, C)
- Low-grade fever (hepatitis A, B, C)
- Loss of appetite (hepatitis A, B, C)
- Fatigue (hepatitis A, B, C)
- Feeling sick to your stomach (hepatitis A, B, C)
- Aching joints (hepatitis )
Prevention
There are vaccines against both hepatitis A and B.
But whether you’re immunized or not, the best protection is to be careful when choosing sexual partners. You can also reduce the risk of hepatitis B by not sharing personal care items that may be contaminated with blood (e.g., razors, toothbrushes) and by ensuring that tattoos and piercings are performed with cleaned and sterilized equipment.
Good personal hygiene can also help prevent the spread of hepatitis A.
Pregnant women are routinely screened for hepatitis B. If it’s found, they may be treated with oral medications during the pregnancy. The baby is given hepatitis B vaccination and also immune globulin, a preparation made from the immune blood of someone who was previously infected.
Antiviral medications such as lamivudine* and peginterferon Alfa, along with some others, can be used to treat some people with chronic hepatitis B. These medications do not cure the condition or stop it from being passed on to others, but they may reduce virus levels and activity, which can help reduce the signs of liver damage.
People who have been diagnosed with hepatitis A or B should avoid alcohol for at least 3 months or until their liver tests and liver functions are normal.
-
Bird Flu
Bird flu, also called avian influenza, is a viral infection that can infect not only birds, but also humans and other animals. Most forms of the virus are restricted to birds.
H5N1 is the most common form of bird flu. It’s deadly to birds and can easily affect humans and other animals that come in contact with a carrier.
Currently, the virus isn’t known to spread via human-to-human contact. Still, some experts’ worry that H5N1 may pose a risk of becoming a pandemic threat to humans.
Symptoms
- cough
- diarrhea
- respiratory difficulties
- fever (over 100.4°F or 38°C)
- headache
- muscle aches
- malaise
- runny nose
- sore throat
Bird flu risk factors
- a poultry farmer
- a traveller visiting affected areas
- exposed to infected birds
- someone who eats undercooked poultry or eggs
- a healthcare worker caring for infected patients
- a household member of an infected person
Prevention
- Different types of bird flu can cause different symptoms. As a result, treatments may vary.
- In most cases, treatment with antiviral medication such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza) can help reduce the severity of the disease. However, the medication must be taken within 48 hours after symptoms first appear.
- The virus that causes the human form of the flu can develop resistance to the two most common forms of antiviral medications, amantadine and rimantadine (Flumadine). These medications shouldn’t be used to treat the disease.
- Your family or others in close contact with you might also be prescribed antivirals as a preventive measure, even if they aren’t sick. You’ll be placed in isolation to avoid spreading the virus to others.
- Your doctor may place you on a breathing machine if you develop a severe infection.
Contact us for:-
-
- IAS coaching in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- UKPCS-UKPSC/UPPCS coaching in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- Current Affairs classes in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- For getting detailed feedback on your answers and improve answer writing
- Phone Number:–9997453844
- Telegram channel : click here
-
- UKPCS Mains Mock Test Series: Lower + Upper Combo - July 2, 2025
- UKPCS 2026 Complete Prelims + Mains Course - June 21, 2025
- UKPCS Mains Lower Test Series 2025 - June 19, 2025
