Hi All,
Oracle IAS presents to you UPPCS Mains 2019 GS paper 1 analysis along with UPPCS Mains GS 1 model answers. In the subsequent posts we will also analyse:
- UPPCS Mains GS 2 paper
- UPPCS Mains GS 3 paper
- UPPCS Mains GS 4 paper
We had also initiated UPPCS Mains test series few months back along with UPPCS Mains Daily answer writing program. Many questions that were part of the initiatives appeared in the UPPCS Mains real paper.
Instructions for UPPCS Mains 2019 GS Paper-1
- UPPSC conducted general studies paper 1 for state civil services mains examination.
- Duration: 3 hours; Maximum Marks: 200
- Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions:
- There are TWENTY questions printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH. Question 1-10 questions carry 8 marks each (125 words) & questions 11-20 carry 12 marks each (200 words)
- All the questions are compulsory.
- Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission Certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QC4) Booklet in the space provided.
- No marks will be given for answers written in a medium other than the authorized one.
- Word limit in questions, wherever specified should be adhered to.
- Any page or portion of the page left blank in the Question-cum-Answer Booklet must be clearly struck off.
UPPCS Mains नोटः
1) कुल 20 प्रश्न दिए गए हैं। खण्ड-अ से 10 प्रश्न लघु उत्तरीय हैं जिनके प्रत्येक उत्तर की शब्द-सीमा 125 तथा खण्ड-ब से 10 प्रश्न दीर्घउत्तरीय हैं जिनके प्रत्येक उत्तर की शब्द सीमा 200 निर्धारित हैं। जो हिन्दी और अंग्रेजी दोनों में छपे हैं।
2) सभी प्रश्न अनिवार्य हैं।
3) प्रत्येक प्रश्न/भाग के लिए नियत अंक उसके सामने दिए गए हैं।
4) प्रश्नों में इंगित शब्द-सीमा को ध्यान में रखें।
5) उत्तर पुस्तिका में खाली छोड़े गए कोई पृष्ठ अथवा पृष्ठ के भाग को पूर्णतः काट दें।
UPPCS Mains Short Answer Questions ::(125 words, 8 marks)
Section – A
1. Explain the role of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in the integration of Princely States of India.
2. Describe the role of Buddhist literature in the creation of world peace.
3. Mahatma Gandhi represents the middle path approach in Indian Politics. Give logical explanation.
4. “Communal violence is instigated by religious fanatics, initiated by anti-social elements, supported by political activists, financed by vested interests.” Comment.
5. Evaluate the changing status of women in India.
6. Discuss the solution to urban problems.
7. Give an account of the minerals found in Uttar Pradesh.
8. Enumerate the core infrastructure elements for Smart City development.
9. Write a note on the Global Warming.
10. Give a geographical account of Bundelkhand as a cultural region.
UPPCS Mains Long Answer Questions ::(200 words, 12 marks)
Section – B
11. “The spine of Indian Economy was badly injured during the 200 years of British Rule.” Explain.
12. Discuss the role of Hitler in bringing about the Second World War.
13. “Revolt of 1857 was a turning point in India History”. Analyse.
14. “Secularism as an orientation and a set of practices is indispensable to India’s future as a liberal democracy.” Discuss.
15. Discuss the impact of globalization on the status of women in India society by citing suitable examples.
16. What is globalization ? Discuss its impact on the social structure of India.
17. Give an account of the primary targets of Uttar Pradesh Tourism Policy (2018).
18. What is an air mass? Describe its chief characteristics.
19. How are volcano, earthquake and tsunami related to each other? Highlight all the possible causes for volcanic eruptions.
20. Mention the factors responsible for the origins of ocean currents and name the currents of the Atlantic Ocean.
UPPCS Mains लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न ::(125 words, 8 marks)
खण्ड – अ
1- सरदार वल्लभभाई पटेल की भारतीय रियासतों के विलीनीकरण में भूमिका को स्पष्ट कीजिए।
2- विश्व शान्ति स्थापना में बौद्ध साहित्य की भूमिका का वर्णन कीजिए।
3- महात्मा गांधी भारतीय राजनीति के मध्यम-मार्गी दृष्टिकोण का प्रतिनिधित्व करते हैं। कर्तपूर्ण व्याख्या कीजिए।
4- ‘‘साम्प्रदायिक हिंसा धार्मिक कट्टरपंथियों द्वारा भड़कायी जाती है, असामाजिक तत्वों द्वारा प्रारम्भ की जाती है, राजनैतिक कार्यकर्ताओं द्वारा प्रोत्साहित की जाती है, निहित स्वार्थों द्वारा वित्तपोषित होती है।’’ टिप्पणी कीजिए।
5- भारत में स्त्रियों की बदलती प्रस्थिति का मूल्यांकन कीजिए।
6- शहरी समस्याओं के समाधान की विवेचना कीजिए।
7- उत्तर प्रदेश में पाये जाने वाले खनिजों का विवरण दीजिए।
8- स्मार्ट सिटी विकास हेतु मूल अधोसंरचनात्मक तत्व बताए।
9- भू-मण्डलीय ऊष्मन पर टिप्पणी लिखिए।
10- बुन्देलखण्ड का एक सांस्कृतिक क्षेत्र के रूप में भौगोलिक विवरण प्रस्तुत कीजिए।
UPPCS Mains दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्न ::(2oo words, 12 marks)
खण्ड – ब
11- ‘‘200 वर्षों के ब्रिटिश शासन ने भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था के मेरुदण्ड को क्षतिग्रस्त कर दिया था।’’ व्याख्या कीजिए।
12- द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध को अवश्यम्भावी बनाने में हिटलर की भूमिका की विवेचना कीजिए।
13- ‘‘1857 का विद्रोह भारतीय भारतीय इतिहास में एक निर्णायक मोड़ था।’’ विश्लेषण कीजिए।
14- ‘‘धर्मनिरपेक्षतावाद अभिमुखन व व्यवहार के एक समुच्चय के रूप में उदारवादी लोकतान्त्रिक भारत के भविष्य के लिए अपरिहार्य है’’ विवेचना कीजिए।
15- भारतीय महिलाओं पर भूमण्डलीकरण के प्रभावों की विवेचना उपयुक्त उदाहरणों की सहायता से कीजिए।
16- वैश्वीकरण क्या है? भारतीय सामाजिक संरचना पर इसके प्रभावों की विवेचना कीजिए।
17- उत्तर प्रदेश की पर्यटन नीति (2018) के प्राथमिक लक्ष्यों का विवरण दीजिए।
18- वायु-राशि क्या है? इसकी प्रमुख विशेषताओं का उल्लेख कीजिए।
19- ज्वालामुखी, भूकम्प और सुनामी आपस में कैसे सम्बन्धित है? ज्वालामुख उद्गार के सम्भावित सभी कारणों पर प्रकाश डालिये।
20- महासागरीय धाराओं की उत्पत्ति के लिए उत्तरदायी कारकों का उल्लेख कीजिए और अन्ध महासागर की जल धाराओं का नाम बताइए।
Uttar Pradesh Mains (UPPCS Mains 2019) paper analysis
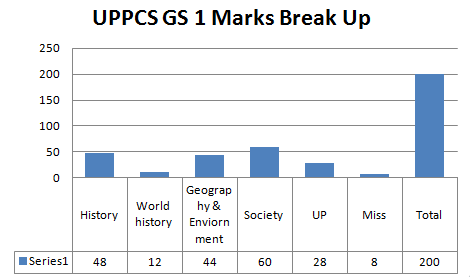
General Observations:-
- Most of the questions were direct and could be answered by standard books
- NCERTs (6 to 12) are more than sufficient but to make your answer dynamic current affairs becomes important
- UP section was also covered in the UPPCS Mains exam. Thus it cannot be ignored.
- Many of the questions were covered in the class UPPCS Mains answer writing practice & test series
- Suggestion: Go through the past UPSC Mains paper post 2012
| UPPCS Mains GS 1 Question number | Subject/syllabus | Difficulty level | Remark/Source |
| 1- Sardar Patel | Modern History | Easy | Test Series – Test 1, Q21 |
| 2- Buddhist literature | Ancient- Culture | Moderate | NCERT, Class notes, Need to be innovative and connect the dots |
| 3- Mahatma Gandhi | Modern History | Moderate | Test series- Test 1, Q3 |
| 4- Communal violence | Society | Moderate | Click here & Test series- Test 1 Q 20 |
| 5- Women status | Society | Easy | Test series – Test 2 Q 19, Bias against women |
| 6- Urban problems | Society | Easy | Test series – test 2- Q11 |
| 7- Minerals in UP | UP | Easy | |
| 8- Smart city | Schemes | Easy | Current affairs class |
| 9- Global warming | Geography and environment | Easy | NCERT |
| 10- Bundelkhand | UP | Moderate | |
| 11- Indian economy | Modern History | Easy | Class notes |
| 12- Hitler | World History | Easy | Norman Lowe, Class notes |
| 13- Revolt of 1857 | Modern History | Easy | NCERT, Class notes |
| 14- Secularism | Society | Moderate | Current Affairs class |
| 15- Globalization and status of women | Society | Easy | Class notes |
| 16- Globalization and Social structure | Society | Moderate | Test series- test 2 Q18 |
| 17- UP tourism policy | UP | Easy | |
| 18- Air mass | Geography | Easy | NCERT |
| 19- Volcano, earthquake | Geography | Easy | NCERT , Test series – Test 1 – Q17
Test 2 – Q2, Q3 |
| 20- Ocean currents | Geography | Easy | NCERT |
UPPCS Mains 2019 GS 1 Model Answers
- Explain the role of SardarVallabhbhai Patel in the integration of Princely states of India.
SardarVallabhbhai Patel was a veteran Gandhian freedom fighter, first Home Minister and deputy PM of India. He used a combination of diplomacy and military power to unite India.
- Diplomacy was used in most cases and most of the 565 princely states joined India on amicable terms and were merged into various states later.
- Travancore, Bhopal, Jodhpur etc were also merged after some initial resistance.
- In case of Junagarh and specially Hyderabad he used military force{1948 Operation Polo} to integrate it into India.
Thus Patel, ably supported by V P Menon, used his experience of dealing with princes{Rajkot Satyagrah} and saved India from Balkanisation. He is thus known as ironman has been immortalized in Statue of Unity
- Describe the role of Buddhist Literature in the creation of world peace
Buddhist literature emphasizes on peace{Shanti}, non-violence{Ahimsa} and friendship{Mitrata/Metta}. Role of Buddhist literature in furthering world peace can be seen in following cases:-
- The pillar inscriptions and rock inscriptions of Ashoka extol virtues of Dhammavijaya{victory by Dhamma} in place of Ghoshavijaya{victory by military means}. It created peace in Indian subcontinent and neighbourhood for a few decades. It also influenced pacifist anti-colonial foreign policy of India after independence
- In modern world, the concept of Panchsheel has been experimented with between India and China for foreign relations based on equality, peace and non-interference. If this policy is adopted by big countries, many conflicts would inevitably end.
- Buddhist literature focuses on inquiry of the self and on application leads to a non-materialistic approach to life, thereby reducing conflicts.
- Mahatma Gandhi represents the middle path approach in Indian politics. Give logical explanation.
Mahatma Gandhi led the freedom struggle during 1919-1947. His approach borrowed practices from all shades of political opinion, religions and regions:-
- In social sphere, advocated end of untouchability but also supported Varnashram dharma.
- In economics, he took donations from capitalists, advocated ‘trusteeship model’, fought for the labourers{Ahmedabad Satyagrah and Textile union} and also wanted development through cottage industries.
- In politics, he was in favour of non-Satyagrah method, but also worked with Communists and Socialists.
- In tactics, he took middle path. He was not bound by constitutional methods, but abhorred violence.
Thus Gandhiji walked a middle path and was able to make Congress more than a Party, and during those years Congress worked as a movement able to include into its fold leaders and sympathisers of different ideologies.
- “Communal violence is instigated by religious fanatics, initiated by anti-social elements, supported by political activists, financed by vested interests.” Comment.
Communalism in South Asia is used to denote the differences between the various religious groups and difference among the people of different community. And generally it is used to catalyse communal violence between those groups. It is a political ideology that divides the people on religious lines.
Religious fanatics fervor religious tensions. It may include:
- Distorting facts and sermons that demonizes the other community
- Mob lynching
- Religious conversion
Politicians have played a villainous role in creating serious communal situations in India. It is manifested in the form of:
- Participation by members of political parties in riots
- Distribution of tickets on religious lines
- Asking for votes and conducting rallies for particular religious groups
External elements having vested interest in India’s instability (including non-state actors) also have a role in worsening the problem of communalism, and making it serious. Egs Pakistan, China in NE etc.
Conclusion
Communalism is a serious issue in India that creates a barrier in its development.
- Evaluate the changing status of women in India.
The status of women is much higher than the ancient and medieval times.
This is exemplified by the following facts:
- Political: The number of women representative has been increasing over the period of time.
- Economic: More women are engaged in paid work outside home in both rural and urban areas
- Social: More women are enrolled in schools and colleges. Moreover Inter caste marriages, divorce has increased. Even the stigma attached to rape has diluted.
The major reasons for improved status are:
- Laws/policies: The government has passed many laws empowering women egs. Reservation of women in local bodies, dowry act, domestic violence act, Stand up India etc.
- Social movement/protests by women organization eg. Nirbhaya movement, anti- alcohol movement etc.
- Self help movement has empowered women at grassroots level.
- Modern education has changed the perception of society towards the role of women.
Conclusion
At present women in India enjoy equal status to men (Art 14, 15). However much needs to be done as still India lies at the bottom of the global gender gap report (108)
-
Discuss the solution to urban problems.
As per official statistics more than 30 % people live in urban areas today and it would increase to 50 % by 2040. Rapid urbanization has led to many problems like over urbanization, pollution, environmental degradation, crime etc.
The solution could be:
- Making villages self sufficient so that no distress migration takes place. Schemes like national rurban mission.
- Decentralizing more power to urban local bodies and giving them autonomy.
- Making cities accessible for the poor affordable housing for poor, providing basic facilities like food, health and education. Slum development should be major component of it. Egs ‘one nation – one ration card’ is a move in the right direction.
- Building sustainable environmental friendly cities that includes mass rapid transport, water recycling , green buildings (GRIHA)
- Population control measures should be introduced. Community policing should be incorporated for increasing incidence of crime.
As per the WHO report Indian cities are one of the most polluted in the world. The need of the hour is to expedite smart city mission and AMRUT .
- Give an account of the minerals found in Uttar Pradesh.
Uttar Pradesh is endowed with natural wealth in abundance. This wealth lies hidden below a variety of rocks of different ages found mostly in the Vindhyan ranges in the South. Minor minerals are found all over the state. The minerals found in Uttar Pradesh include:-
- limestone which is found in Guruma-Kanach-Bapuhari in Mirzapur district and Kajrahat in Sonebhadra district;
- dolomite is found in Mirzapur, Sonebhadra and Banda districts,
- glass-sand is found in Karchhana of Allahabad district, Karwi in Banda district and Mau district
- Marble is found in in Mirzapur and Sonebhadra;
- bauxite in Rajhgewan in Banda district;
- non-plastic fireclay in Bansi and Makri-Khoh area of Mirzapur district;
- Uranium is found in Lalitpur district in Bundelkhand.
- Barytes and Edalusite are found in the districts of Mirzapur and Sonebhadra.
- Sand-stone, pebbles, reh, salt punter, maurang, sand and other minor minerals are also found in the State.
- Enumerate the core infrastructure elements for Smart City development.
A smart city uses information and communication technologies (ICT) to increase operational efficiency, share information with the public and improve both the quality of government services and citizen welfare.
Core infrastructure elements are:
- Adequate Water Supply
- Assured Electricity Supply
- Sanitation, including Solid Waste Management
- Efficient Urban Mobility and Public Transport
- Affordable housing, especially for the poor
- Robust IT connectivity and digitalization
- Good governance, especially e-Governance and citizen participation
- Sustainable environment
- Safety and security of citizens, particularly women, children and the elderly, and
- Health and Education.
Conclusion
The GOI has come up with the smart city mission that aims in developing 100 smart cities in India in coming years
- Write a note on the Global Warming.
Global Warming is the increase in Earth’s mean surface temperature because of the effect of greenhouse gases. These gases absorb long wave radiations and warm the atmosphere, and this process is called as Greenhouse effect. The major green gas houses are CO2, NO2 etc. Anthropogenic factors are the main reason for global warming.
Impacts :
- Rising Sea level: Flooding of fresh water marshlands, low-lying cities etc
- Changes in rainfall patterns: Some areas experience droughts while some experience recurrent flooding.
- Melting of the ice peaks and glaciers: Due to melting of the ice peaks, there is loss of habitat near the poles.
- Spread of disease: There is spread of diseases like malaria due to migration to newer and currently warmer regions.
- Thinning of Coral Reefs due to warming seas as well as acidification because of carbonic acid formation: Almost one-third of coral reefs are now severely damaged by warming seas.
- Give a geographical account of Bundelkhand as a cultural region
Bundelkhand cultural region is divided between the states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, with the larger portion lying in MP. Its geographical features are:-
- Bundelkhand lies between the Indo-Gangetic Plainto the north and the Vindhya Range to the south.
- The plains of Bundelkhand are intersected by three mountain ranges of the Vindhyas which are not very high{highest approx.. 600 m }. There are isolated with steepslope where local kings made forts.
- The principal rivers are the Sindh, Betwa, Kenand Chambalwhich follow slope to northeast and meet Yamuna River.
- In these streams, the depression of their channels and height of their banks make them unsuitable for irrigation, which is conducted by means of ponds and tanks.
- These artificial lakes are usually formed by throwing embankments across the lower extremities of valleys, and thus arresting and impounding the waters flowing through them.
- “The spine of Indian Economy was badly injured during the 200 years of British Rule”. Explain
British ruled parts of India from 1757 to 1947. According to Angus Maddison, from 1700 to 1950, India’s share in world GDP went from around 25% to less than 5%. This shows the extent of economic deprivation in India which impacted all sections of people:-
- British land revenue policies {Zamindar, Ryotwari and Mahalwari} ruined Indian farmers and millions of people died in famines during British period. Also they exploited farmers who cultivated cash crops {e.g. indigo in Bengal and Bihar}.
- The artisans, specially those who worked in India’s textile industry were ruined by British tax and trade policies. India was deindustrialized and became just an exporter of raw material and agri-commodities.
- British established industries and railways in India. But that also served British interests as the profit was repatriated and not invested in India.
The results were:-
- Widespread poverty in India as documented by DadabhaiNauroji {Poverty and Unbritish Rule in India} and explained by economic nationalists like R. C. Dutt, Gokhale etc.
- The trade structure of India changed with bulk of trade with Britain. We became importers of British goods and exporters of raw materials thus at a lower level in value chain.
- India’s wealth was drained into Britain by various devices like Home Charges, investments etc.
The last famine in India was in 1943 in Bengal which killed 3 million people. India’s life expectancy at independence was only 33 years. It all shows impact of British economic policies on India.
- Discuss the role of Hitler in bringing about the second World War.
Hitler, the leader of Germany during 1933-1945 is sometimes blamed for starting World War 2 in 1939 due to following reasons:-
- It is argued that he wanted to destroy Communism and wanted to control USSR permanently, which could not be done without a major war. He had written about this in his book: Mein Kempf.
- He ignored the treaty of Versailles and increased the strength of his army, navy and airforce.
- His actions in Czechoslovakia showed his desire for expansion, although at that time the allies appeased him.
- Finally, he attacked Poland from all sides and not just the city of Danzig and the corridor, which showed that he would not stop at just the present claims.
Some other historians say that Hitler may have wanted just a limited war with Poland and Russia, rather than a World War. Initially he got his claims in Czechoslovakia by cooperation of allies and may have believed that similar tactics could be used in Poland and expected a short war with Russia.
The power structure in Europe after World War 1 had many issues:-
- Versailles treaty had blamed Germans for war and this along with hefty reparations imposed on them, made Germans bitter and unltra-nationalist.
- Failure of League of Nations encouraged Germans
- The Economic crisis of 1920s and 30s ensured that a populist like Hitler rises to the top.4
Thus Hitler was just a product of his times and the war also had some deeper reasons.
- “Revolt of 1857 was a turning point in Indian History.” Analyse
The revolt of 1857, called first war of Independence by Savarkar, had a huge geographical and societal spread. It encompassed areas from Delhi to Bengal and Uttarakhand to Gwaliar region with particular intensity. It had participation of soldiers, peasants, landlords/princes, artisans of Hindu as well as Muslim faith. It was a turning point because:-
- The East India Company was relieved of its duties and Crown directly took control of Indian Empire and started rule through Viceroy, personal representative of Crown.
- British changed the policy and started taking native kings and zamindars elements into their confidence. E.g.: They abolished ‘Doctrine of Lapse.
- In social policy they stopped progressive policies{e.g. Sati abolition, widow remarriage} and promoted orthodoxy. As 1857 was a joint Hindu-Muslim effort, they started policy of divide and rule which ultimately led to partition.
- There were changes in administration and Indians started getting in councils and slowly in bureaucracy. However army was kept more under British control.
- The movements after 1857 focussed mostly on constitutional and peaceful methods rather than violent means.
However, the economic loot of the country continued and even became more efficient. In 1857, the old feudal order in India was made powerless. It ultimately led to emergence of national movement which derived inspiration from revolt of 1857.
- “Secularism as an orientation and a set of practices is indispensable to India’s future as a liberal democracy” Discuss
Secularism in the Indian context is the positive connotation of the word, unlike the west where there is strict separation of religion from state. Indian secularism follows ‘Sarva Dharma Sambhav’.
It is practiced in the following manner:
1.The State shall not attach itself to any one religion, which will thereby establish itself as the State religion.
- All citizens are granted the freedom of religious belief.
3.The State will ensure equality among religious groups by ensuring that one group is not favoured at the expense of the other.Correspondingly, theminorities will not be discriminated in any way.
Constitutional provisions
- Article 25- 28- It is the foundation of secularism in India
- Article 14,15 – Right to equality to all citizens
- Artticle 29- 30 – constitutional protections to safeguard the religious customs and practices of the minorities and enables them to administer their educational institutions as a fundamental right.
Secularism is important for India for the following reasons:
- It enables people of different religions to live in civility with respect for all faiths.
- It is a part of democracy, which grants equal rights.
- It safe guards democracy by limiting the powers of the majority and
- It protects the equal rights of minorities to citizens
Secularism and liberal Democracy
Secularism is invaluable for a society like India which is characterized with religious diversity. Secularism regulates the relationship between the State and various religious groups. In a secular State, all groups are treated equally and the State is not aligned to any religion. No person shall be discriminated against on the ground that he or she belongs to a particular religion. Secularism becomes meaningful only when it refers to democratic equality. No society is secular unless it is committed to democratic principles of freedom and equality.
Conclusion
Secularism allows us to live in some measure of civility. Secularism is therefore desirable for a plural society like India.
- Discuss the impact of Globalisation on the status of women in Indian Society by citing suitable examples.
Over the ages, women in India have faced the problems such as patriarchy and inadequate access to productive resources. However, the new circumstances created by globalization are diverse, encompass all women in the country and cover almost all aspects of their life. Some of these are as follows:
Positive Impacts
Changing role in work
Globalization has undermined the traditional role of women in homemaking, farming, livestock, animal husbandry, handicrafts, handlooms etc and resulted in a relatively better environment and more jobs for women. It has affected both the quantity and the quality of work available to the majority of women in India.
Changing role in Family, Marriage, Caste
As women take up jobs and achieve social mobility, they have also begun to stand up for their rights. As nuclear families have become more common, it has become easier for women to assertively claim their rights and ask for equality in an environment. Marrying within the same caste has become less important.
Other Positive Impacts
- Prospects of higher and quality education have become feasible
- Employment in technological and other advanced sectors, which have global bearing, has opened up for suitably qualified women.
- With changing attitude towards women, especially in the urban areas, women enjoy more egalitarian set of gender relationship.
- Attitudinal changes towards women’s role in the family due to good education, benefits of family planning and health care, child care, good job opportunities etc. will surely help in the development of more confident and healthy women.
Negative Impacts
Globalization has increased the number of low paid, part time and exploitative jobs for women. Similarly, male migration from rural areas to urban centres has put the women under triple burden of home making, farming and job in rural sector. At the same time, migration of women for economic reasons has led to increased exploitation including sexual exploitation and trafficking.
Conclusion
Globalisation has major positive impact on status of women. Moreover, the state policies have been favorable for women social mobility.
- What is globalisation? Discuss its impacts on the social structure of India.
Globalization is the movement of people, ideas and capital across the transnational borders. Globalization is nothing new to India. For centuries, people have migrated here, bringing their own cultures, social norms, value systems and ways of life. However, the latest wave of globalization that began post 1990 after LPG reforms.
Impact of globalization on social structure of India:
- Decrease in family values: Increasing mobility of younger generation in search of new employment and educational opportunities allegedly weakened the family relations. The traditional joint famil is being replaced by nuclear families.
- Individualism is increasing while collective social life is in decline. The traditional neighborhood feeling is being replaced by isolation and anonymity.
- Social hierarchy: The traditional form of social structure marked by caste system is getting diluted in various spheres of life. Class as a social hierarchy is gaining prominence.
- Social mobility: With globalization social mobility and geographical mobility has increased. The social system has become more open.
- Patriarchy: Patriarchy as a social system where men dominates over females is being challenged. This is due to increase opportunities to women outside home and better education.
- Complicated married life : Married men and women are staying separately at far off places on account of their jobs which are providing lucrative pay packets and financial security. Apart from this, single living, single parents (person who had children beyond wed lock) and living together without any formal marriage are also found in the society.
Conclusion
The Indian social system is being transformed under the influence of modernity brought about by the forces of globalization where traditional structure is being challenged and emancipating many persecuted social groups egsDalits, women etc.
- Give an account of the primary targets of UP Tourism Policy{2018}.
Tourism can be a sunshine sector in UP. UP has a plethora of places of religious, historical, ecological and archaeological importance. The targets of UP Tourism policy 2018 are:-
- To become the most prefrential tourist destination by 2023.
- To achieve annual increase of 15 % domestic tourist arrival and 10% foreign tourist arrival
- To provide employment to 5 lakh people per year
- Training to 10000 tourism servise provider over next 5 years
- To convert 10 heritage sites into heritage hotels per year
- To attract 1 lakh tourists to national parks
- To imrove regional connectivity via road, rail and air
- To promote city wise events as per pre defined calendar
- To improve local enterepessnurship through tourism events like deepotsav, international ramanyana conclave, geetamahotsavetc
Conclusion: PRASAD and SwadeshDarshan
- What is air mass? Describe its chief characteristics.
n air mass is a large body of air whose physical properties especially temperature and moisture content are relatively uniform horizontally.
- Some of the well-known source regions are sub-tropical and tropical oceans, i.e., low-latitude deserts like the Sahara in the summer and the continental interiors’ especially those of North America and Eurasia in the winter.
- Air masses can be grouped according to source regions, air masses may broadly be grouped under two categories–tropical and polar further sub division can be done according to the continental and maritime air masses
- Maritime air masses contain high humidity and produce a large amount of precipitation.
- Continental air masses are dry and produce less amount of precipitation
CHARACTERISTICS OF AIR MASS
- It must be large. A typical air mass is more than 1600 kms across and several kms deep.
- At any given altitude in the air mass, its physical characteristics primarily temperature, humidity, and stability are relatively homogeneous.
- It must be distinct from the surrounding air, and when it moves, it must retain its original characteristics and not be torn apart by differences in airflow.
-
- How are volcano, earthquake and tsunami related to each other? Highlight all the possible causes for volcanic eruptions.
FOLLOWING ARE THE RELATION SHIP BETWEEN EARTHQUAKE, TSUNAMI AND VOLCANOS
- Earth quake are considered to be the reason behind all major tsunamis of the world, earthquake posses large amount of energy in waves forms which displaces large amount of water resulting in the huge tsunamis.
- Volcanic eruption causes the earthquakes which may also generate tsunamis, also the debris and pyroclast material avalanche when moving with Very high speed crashes in the sea it may result in huge tsunami waves.
- Most earthquakes directly beneath a volcano are caused by the movement of magma. The magma exerts pressure on the rocks until it cracks the rock. Then the magma squirts into the crack and starts building pressure again. Every time the rock cracks it makes a small earthquake.
Causes of volcanic eruptions
- The first and foremost reason is the crustal disturbance in the zone of weakness due to deep faulting or mountain folding.
- Heat generated by degeneration of radioactive elements inside the earth which causes an increase in temperature inside the earth, thus causing eruptions of the inside materials.
- Reduction in pressure of rock due to formation of fractures causing the formation of magma.
- Formation of gases due to high temperature.
- Sometimes, the earthquakes may expose the fault zones in the rock strata through which the Magma can escape to the earth s surface leading to volcanic eruptions.
-
- Mention the factors responsible for the origins of ocean currents and name the currents of the Atlantic Ocean.
MAIN FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR THE ORIGIN OF OCEAN CURRENTS ARE :
- Planetary winds:Planetary winds are the principal cause of the origin of ocean currents. Such winds drive surface water along with them.
- Difference of density and salinity:Difference of density and salinity in ocean water motivates denser waters to sink and move as undercurrents; whereas lighter waters move towards the denser water as surface currents.
- The rotation of the Earth:The rotation of the Earth causes Coriolis force which affects the direction of movement of water and leads to formation of ocean currents.
- The shape of coastline:The shape of coastline is also an important factor that affects the current in the oceans.
- Frictional force:Movement of water through the oceans is slowed by friction, with surrounding fluid moving at a different velocity which leads to a difference in the speed of water and generates current.
The currents of the Atlantic Ocean can be grouped according to warm and cold currents.WARM CURRENTS OF ATLANTIC OCEAN ARE:
- South equatorial current
- North equatorial current
- Gulf Stream
- Brazil current
COLD CURRENTS OF THE ATLANTIC OCEAN ARE:
- Benguela current
- Falkland current
- Peru Current
- Canary current
- Labrador Current
- South Atlantic drift
Contact us for:-
- IAS coaching in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- UKPCS/UPPCS Mains coaching in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- Current Affairs classes in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- For getting detailed feedback on your answers and improve answer writing
- Phone Number:–9997453844
