Oracle IAS, the best coaching institute for UPSC/IAS/PCS preparation in Dehradun brings to you UKPCS Science Life Sciences (paper 6- Respiratory system.
The respiratory system plays a vital role in the body, by providing your cells with much needed oxygen, as well as excreting carbon dioxide, which can be deadly if allowed to accumulate. Major parts of the system include the airways, the lungs, and the muscles of respiration. This article will explain anatomy of the respiratory system, detailing the organs involved as well as the things that can go wrong
.Anatomy of Respiratory System: Organs and Functions
The three major parts of the respiratory system all work together to carry out their task. The airways (nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx etc.) allow air to enter the body and into the lungs. The lungs work to pass oxygen into the body, whilst removing carbon dioxide from the body. The muscles of respiration, such as the diaphragm, work in unison to pump air into and out of the lungs whilst breathing.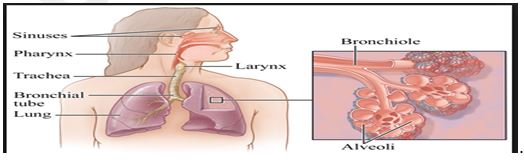
| Respiratory Organs | Description | Function |
| Nose and Nasal Cavity | The nose is the primary opening for the respiratory system, made of bone, muscle, and cartilage. The nasal cavity is a cavity within your nose filled with mucus membranes and hairs. | The nose is used to inhale air into the body. The nasal cavity warms the air as it enters, acting as filtration and purifying the air by removing any dust, pollen, and other contaminants, before it passed to the inner body. |
| Mouth | Also called the oral cavity, the mouth is the secondary exterior opening for the respiratory system. Most commonly, the majority of respiration is achieved via the nose and nasal cavity, but the mouth can be used if needed. | Inhaling air through the mouth allows more inhalation, as the oral cavity is far larger than the nasal cavity. The air also has less distance to travel, meaning more air can enter your body and be used faster. The oral cavity has no hairs or filtering techniques, meaning the air you inhale does not undergo the filtration process. |
| Pharynx | Also called the throat, the pharynx is a funnel of muscle that extends from the respiratory openings to the esophagus and larynx. | Air that is inhaled enters the pharynx, where it descends into the larynx via a diversion from the epiglottis. As the pharynx is used for swallowing food as well as breathing, the epiglottis ensures that air can pass into the trachea, and that food enters the esophagus. |
| Larynx | Also known as the voice box, the larynx is situated below the pharynx, in the anterior portion of the neck. | Aside from allowing us the ability of speech, the larynx also acts as a defense mechanism. If any food passes into the esophagus when swallowing, the larynx produces a strong cough reflex. |
| Trachea | Also known as the wind pipe, the trachea is a tube made of cartilage rings that are lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. | The main respiratory function of the trachea is to provide a clear and unhindered airway for air to enter and exit the lungs. Inside the trachea, small hairs reside upon the inner walls. These hairs catch dust and other contaminants from inhaled air, which are later expelled via coughing. |
| Bronchi | The bronchi are two tubes stemming off of the end of the trachea. Each tube is connected to a lung. | The bronchi connect the wind pipe to the lungs, allowing air from external respiratory openings to pass efficiently into the lungs. Once in the lungs, the bronchi begin to branch out into secondary, smaller bronchi, coined tertiary bronchi. |
| Bronchioles | Tertiary bronchi divide to even smaller, narrower tubes known as bronchioles. | Bronchioles lead to alveolar sacs, which are sacs containing alveoli. |
| Alveoli | Alveoli are hollow, individual cavities that are found within alveolar sacs. | Alveoli have extremely thin walls, which allows the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide to take place within the lungs. There are estimated to be three million alveoli in the average lung. |
| Diaphragm | The diaphragm is an important muscle of respiration which is situated beneath the lungs. | The diaphragm contracts to expand the space inside the thoracic cavity, whilst moving a few inches inferiorly into the abdominal cavity. Whilst this is happening, the intercostal muscles also contract, which moves the rip cage up and out. The contractions force air into the lungs, by creating a negative pressure through expansion. |
Contact us for:-
- IAS coaching in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- UKPCS/UPPCS/UPPSC Mains coaching in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- Current Affairs classes in Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
- For getting detailed feedback on your answers and improve answer writing
- Phone Number:–9997453844
- UKPSC प्रारंभिक परीक्षा स्टडी मटेरियल 2026 (Upper & Lower) | Oracle IAS - January 3, 2026
- UKPCS 2026 प्री परीक्षा कोर्स : छात्रवृत्ति टेस्ट: Oracle IAS - December 30, 2025
- UKPSC 2026 के लिए उत्तराखंड प्रारंभिक परीक्षा कोर्स 2026 || Oracle IAS - December 15, 2025
