Oracle IAS, the best coaching institute for UPSC/IAS/PCS preparation in Dehradun brings to you UKPCS Science Life Sciences (paper 6)- Male Reproductive System.
The reproductive system or genital system is a system of sex organs within an organism which work together for the purpose of sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. In this post we will discuss the Male reproductive system.
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The male reproductive system includes the scrotum, testes, spermatic ducts, sex glands, and penis. These organs work together to produce sperm, the male gamete, and the other components of semen. These organs also work together to deliver semen out of the body and into the vagina where it can fertilize egg cells to produce offspring.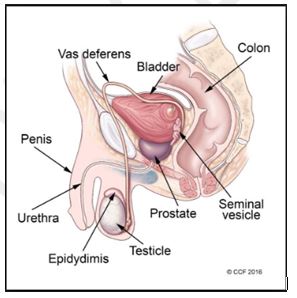
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
Scrotum
The scrotum is a sac-like organ made of skin and muscles that houses the testes. It is located inferior to the penis in the pubic region. The scrotum is made up of 2 side-by-side pouches with a testis located in each pouch.
Testes
The 2 testes, also known as testicles, are the male gonads responsible for the production of sperm and testosterone. The testes are ellipsoid glandular organs around 1.5 to 2 inches long and an inch in diameter. Each testis is found inside its own pouch on one side of the. The inside of the testes is divided into small compartments known as lobules. Each lobule contains a section of seminiferous tubule lined with epithelial cells. These epithelial cells contain many stem cells that divide and form sperm cells through the process of spermatogenesis.
Epididymis
The epididymis is a sperm storage area that wraps around the superior and posterior edge of the testes. Sperm produced in the testes moves into the epididymis to mature before being passed on through the male reproductive organs. The length of the epididymis delays the release of the sperm and allows them time to mature.
Spermatic Cords and Ductus Deferens : Within the scrotum, a pair of spermatic cords connects the testes to the abdominal cavity. The spermatic cords contain the ductus deferens along with nerves, veins, arteries, and lymphatic vessels that support the function of the testes. The ductus deferens, also known as the vas deferens, is a muscular tube that carries sperm superiorly from the epididymis into the abdominal cavity to the ejaculatory duct.
Seminal Vesicles
The seminal vesicles are a pair of lumpy exocrine glands that store and produce some of the liquid portion of semen. The seminal vesicles are about 2 inches in length and located posterior to the urinary bladder and anterior to the rectum. The liquid produced by the seminal vesicles contains proteins and mucus and has an alkaline pH to help sperm survive in the acidic environment of the vagina. The liquid also contains fructose to feed sperm cells so that they survive long enough to fertilize the oocyte.
Ejaculatory Duct
The ductus deferens passes through the prostate and joins with the urethra at a structure known as the ejaculatory duct. The ejaculatory duct contains the ducts from the seminal vesicles as well. During ejaculation, the ejaculatory duct opens and expels sperm and the secretions from the seminal vesicles into the urethra.
Urethra
Semen passes from the ejaculatory duct to the exterior of the body via the urethra, an 8 to 10 inch long muscular tube. The urethra passes through the prostate and ends at the external urethral orifice located at the tip of the penis. Urine exiting the body from the urinary bladder also passes through the urethra.
Penis
The penis is the male external sexual organ located superior to the scrotum and inferior to the umbilicus.The function of the penis is to deliver semen into the vagina during sexual intercourse. In addition to its reproductive function, the penis also allows for the excretion of urine through the urethra to the exterior of the body.
Semen
Semen is the fluid produced by males for sexual reproduction and is ejaculated out of the body during sexual intercourse. Semen contains sperm, the male reproductive gametes,.These sperm cells fertilize oocytes inside the female fallopian tubes.
Printed notes topic wise – Contact us
Cost- Rs.5000/- (including shipping)
(~2500+ pages)
UKPCS Mains Study Material subject wise
The notes are strictly as per UKPCS syllabus (topic wise):
Individual Polity Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual S&T Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual Geography Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual Economics Cost: Rs. 1000/- (including shipping)
Individual Ethics Cost: Rs. 1000/- (including shipping)
Individual History Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Contact us for:-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Upper Mains UKPCS Classroom program
- UKPCS Upper Test Series
- UKPCS Lower Test Series
- UKPCS Lower Classes
- UKPCS Past year papers
- Phone Number:–9997453844
- Telegram channel : click here
-
-
-
-
-
- UKPCS Mains Mock Test Series: Lower + Upper Combo - July 2, 2025
- UKPCS 2026 Complete Prelims + Mains Course - June 21, 2025
- UKPCS Mains Lower Test Series 2025 - June 19, 2025
