Oracle IAS, the best coaching institute for UPSC/IAS/PCS preparation in Dehradun brings to you UKPCS Science (paper #6).
Working of the Eye
The light rays coming from the object enter the eyes through pupil and falls on eye lens. The eye lens then converge the light rays and produce an image of the object on retina which is real and inverted. Retina has large number of light sensitive cells which can generate electrical signals. After the image is formed on the retina it sends electrical signals to the brain and we have a sensation of image. Also, even though the image formed on retina is inverted out mind interprets it as erect.
So, eye lens is the convex lens and retina is the screen of the eye.
Function of iris and pupil
The function of iris is to adjust the size of the pupil. If the amount of light entering the eye is less then pupil expands so that more light can enter the eye and in case the amount of light entering the eye is large then pupil contracts.
The adjustment of the size of pupil takes some time and this is the reason when we go outside in the sunlight from a dark room we feel glare in our eyes or if we enter a dark room after coming from outside we see things clearly after some time.
How do we see colours?
The light sensitive cells in the retina of our eye are of two shapes; rod shape and cone shape. The function of rod shaped cells is to respond to the brightness of light. And the function of cone shaped cells is to make us see colours and distinguish between them.
Seeing distant and nearby objects
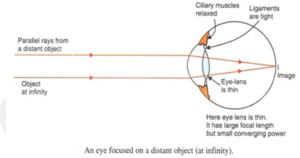
- Distant objects: When the rays of light are coming from distant object they are diverging at the beginning but become parallel when they reach our eye. Therefore to see a distant object, we need to have a convex eye-lens of low converging power to focus them to form an image on the retina of the eye. The convex eye-lens of low converging power has large focal length and is quite thin.
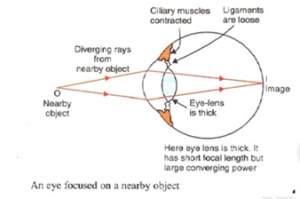
- Nearby objects: When the rays of light are coming from nearby object they diverge when they reach our eyes. Therefore, to see a nearby object we need to have a convex eye-lens of high converging power so as to focus and form an image on the retina. Convex eye-lens with high converging power has short focal length and is thick.
Power of accommodation of the eye
The ability of the eye to focus distant as well as nearby objects clearly on the retina of the eye is called accommodation.
When our eyes see distant objects then the ciliary muscles are relaxes and the focal length is maximum in this position. The eye-lens then converge the parallel rays of light to form an image of the distant object on retina. When the eye see distant object they are said to be unaccommodated.
And when our eyes see nearby objects then the ciliary muscles get stretched and its focal length decreases. Due to this, the converging power of the eye lens increases and the diverging rays of light coming from object converge to form an image on retina. When the eyes see nearby object they are said to be accommodated.
The power of accommodation of a normal eye that enables it to see clearly an object is as close as 25 cm and as far as at infinity.
Value Addition UKPCS Mains : Uttarakhand Special (Click Here)
UKPCS Mains Study Material subject wise
The notes are strictly as per UKPCS syllabus (topic wise):
Individual Polity Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual S&T Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual Geography Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual Economics Cost: Rs. 1000/- (including shipping)
Individual Ethics Cost: Rs. 1000/- (including shipping)
Individual History Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
