Concept of an Ecosystem:
The term ecosystem was coined in 1935 by the Oxford ecologist Arthur Tansley to encompass the interactions among biotic and abiotic components of the environment at a given site. The living and non-living components of an ecosystem are known as biotic and abiotic components, respectively.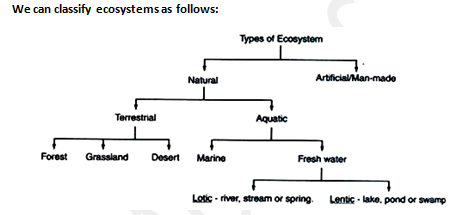
Smith (1966) has summarized common characteristics of most of the ecosystems as follows:
- It is a major structural and functional unit of ecology.
- The structure ois related to its species diversity in the sense that complex ecosystem have high species diversity.
- The function of ecosystem is related to energy flow and material cycles within and outside the system.
- The relative amount of energy needed to maintain an ecosystem depends on its structure. Complex ecosystems needed less energy to maintain themselves.
- Each ecosystem has its own energy budget, which cannot be exceeded.
- Adaptation to local environmental conditions is the important feature of the biotic components of an ecosystem, failing which they might perish.
- The function of every ecosystem involves a series of cycles, e.g., water cycle, nitrogen cycle, oxygen cycle, etc. these cycles are driven by energy.
Types of Ecosystem:
We can classify ecosystems as follows:
(a) Natural Ecosystems:
These are capable of operating and maintaining themselves without any major interference by man.
A classification based on their habitat can further be made:
- Terrestrial: forest, grassland and desert.
- Aquatic: fresh water ecosystem, viz. pond, lake, river and marine ecosystems, viz. ocean, sea or estuary.
(b) Artificial Ecosystem:
These are maintained by man. These are manipulated by man for different purposes, e.g., croplands, artificial lakes and reservoirs, townships and cities.
Basic Structure of an Ecosystem:
Each has a non-living (abiotic) and living (biotic) components.
Each has a non-living (abiotic) and living (biotic) components.
Abiotic Components:
Basic inorganic compounds of an organism, habitat or an area like carbon dioxide, water, nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, etc. that are involved in the material cycles are collectively called as abiotic component.
Whereas, organic components e.g., proteins, amino acids, carbohydrates and lipids that are synthesized by the biotic counterpart of an ecosystem make the biochemical structure of the ecosystem. The physical environment, viz. climatic and weather conditions are also included in the abiotic structure.
Biotic Components:
From the trophic (nutritional) point of view, an ecosystem has autotrophic (self-nourishing) and a heterotrophic (other nourishing) components:
(a) Autotrophic component (Producers):
This component is mainly constituted by the green plants, algae and all photosynthetic organisms. Chemosynthetic bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria, algae, grasses, mosses, shrubs, herbs and trees manufacture food from simple inorganic substances by fixing energy and are therefore called as producers.
(b) Heterotrophic component (Consumers):
The members of this component cannot make their own food. They consume the matter built by the producers and are therefore called as consumers. They may be herbivores, carnivores or omnivores. Herbivores are called as primary consumers whereas carnivores and omnivores are called as secondary consumers.
(c) Decomposers:
Heterotrophic organisms chiefly bacteria and fungi that breakdown the complex compounds of dead protoplasm, absorb some of the products and release simple substances usable by the producers are called as decomposers or reducers. Collectively we call them as micro consumers.
Value Addition UKPCS Mains : Uttarakhand Special (Click Here)
UKPCS Mains Study Material subject wise
The notes are strictly as per UKPCS syllabus (topic wise):
Individual Polity Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual S&T Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual Geography Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual Economics Cost: Rs. 1000/- (including shipping)
Individual Ethics Cost: Rs. 1000/- (including shipping)
Individual History Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
- UKPCS Upper Mains 2024 Study Material : Prepared by Experts Topic wise - April 6, 2024
- UKPSC Mains 2024:New Syllabus Pattern - April 6, 2024
- Oracle IAS’s Mentorship Program for UKPCS 2024 Pre Exam - March 21, 2024
