Food Web
All life needs energy. Whether living organisms make energy themselves or get it from the food they hunt, they need it to maintain and repair their bodies. Reproduction, hunting, growth, cell division, and metabolism are all processes that require energy.
The sun is the ultimate source of energy for life on Earth. Without it, nothing would be able to survive. As a result, living things have evolved special ways to harness the energy of the sun and use it for their own well-being. They have also developed special relationships and interactions that allow energy to be transferred. Once the energy has been captured, it gets passed around through the various organisms in a particular area. This transfer of energy is called a food web.
In their simplest form, food webs are made of food chains.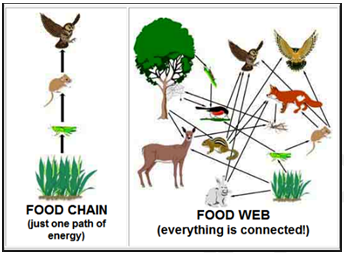
Food Chains
A food chain is the sequence of who eats whom in a biological community (an ecosystem) to obtain nutrition. A food chain starts with the primary energy source, usually the sun or boiling-hot deep sea vents. The next link in the chain is an organism that make its own food from the primary energy source — an example is photosynthetic plants that make their own food from sunlight (using a process called photosynthesis) and chemosynthetic bacteria that make their food energy from chemicals in hydrothermal vents. These are called autotrophs or primary producers.
Next come organisms that eat the autotrophs; these organisms are called herbivores or primary consumers — an example is a rabbit that eats grass.
The next link in the chain is animals that eat herbivores – these are called secondary consumers — an example is a snake that eat rabbits.
In turn, these animals are eaten by larger predators — an example is an owl that eats snakes.
The tertiary consumers are are eaten by quaternary consumers — an example is a hawk that eats owls. Each food chain end with a top predator, and animal with no natural enemies (like an alligator, hawk, or polar bear).
Trophic Levels
The trophic level of an organism is the position it holds in a food chain.
- Primary producers (organisms that make their own food from sunlight and/or chemical energy from deep sea vents) are the base of every food chain – these organisms are called autotrophs.
- Primary consumers are animals that eat primary producers; they are also called herbivores (plant-eaters).
- Secondary consumers eat primary consumers. They are carnivores (meat-eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants).
- Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers.
- Quaternary consumers eat tertiary consumers.
- Food chains “end” with top predators, animals that have little or no natural enemies.
When any organism dies, it is eventually eaten by detrivores (like vultures, worms and crabs) and broken down by decomposers (mostly bacteria and fungi), and the exchange of energy continues. Some organisms’ position in the food chain can vary as their diet differs.
Economic botany
Economic botany is the study of the relationship between people (individuals and cultures) and plants. Economic botany intersects many fields including established disciplines such as agronomy, anthropology, archaeology, chemistry, economics, ethnobotany, ethnology, forestry, genetic resources, geography, geology, horticulture, medicine, microbiology, nutrition, pharmacognosy, and pharmacology. This link between botany and anthropology explores the ways humans use plants for food, shelter, medicines, textiles, and more.
Value Addition UKPCS Mains : Uttarakhand Special (Click Here)
UKPCS Mains Study Material subject wise
The notes are strictly as per UKPCS syllabus (topic wise):
Individual Polity Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual S&T Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual Geography Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
Individual Economics Cost: Rs. 1000/- (including shipping)
Individual Ethics Cost: Rs. 1000/- (including shipping)
Individual History Cost: Rs. 1500/- (including shipping)
- UKPCS 2026 Complete Prelims + Mains Course - June 21, 2025
- UKPCS Mains Lower Test Series 2025 - June 19, 2025
- UKPCS Lower Mains Full Course 2025 by Oracle IAS - June 19, 2025
